Lamina is a general anatomical term meaning "plate" or "layer". It is used in both gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy to describe structures.
Some examples include:
- The laminae of the thyroid cartilage: two leaf-like plates of cartilage that make up the walls of the structure.
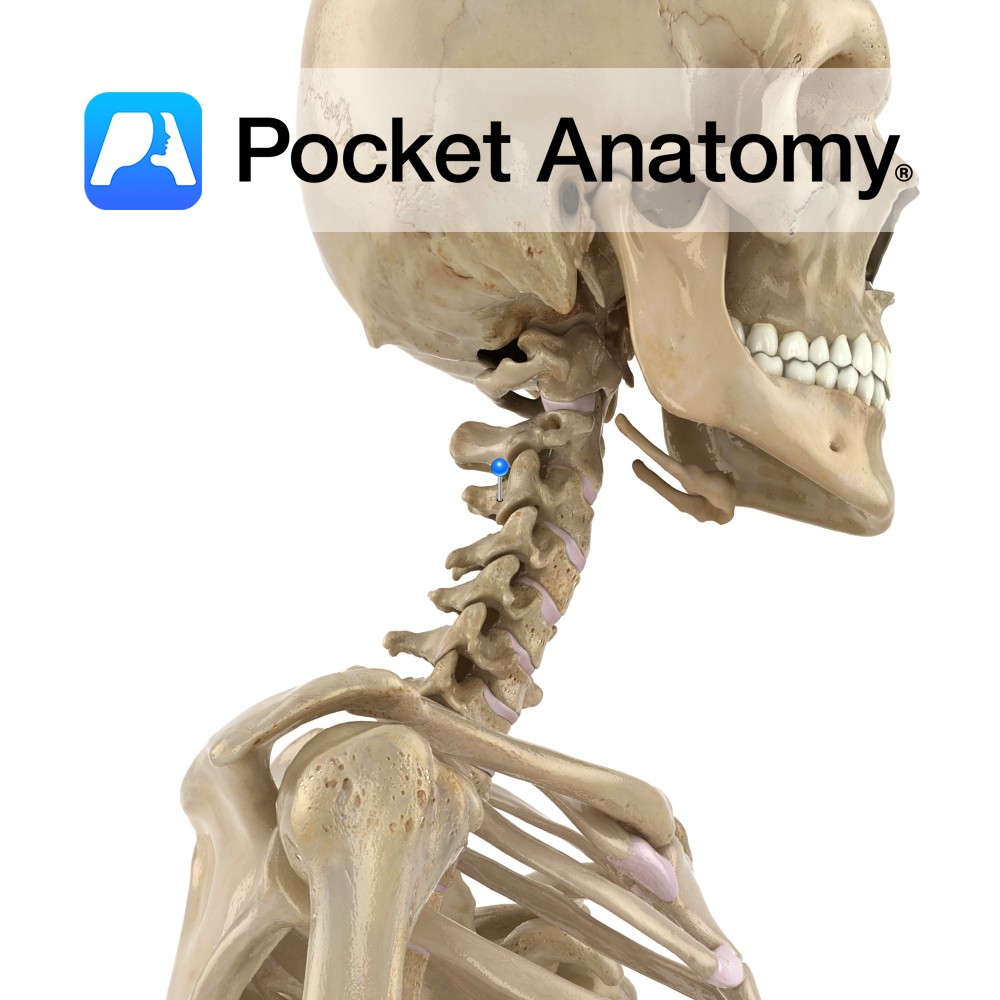
- The vertebral laminae: plates of bone that form the posterior walls of each vertebra, enclosing the spinal cord.
- The laminae of the thalamus: the layers of thalamus tissue.
- The lamina propria: a connective tissue layer under the epithelium of an organ.
- The nuclear lamina: a dense fiber network inside the nucleus of cells.
- The lamina affixa: a layer of epithelium growing on the surface of the thalamus.
- The lamina of Drosophila is the most peripheral neuropil of the insect visual system.
- Lamina cribrosa with two different meanings.
- Osseous spiral lamina, a feature of the bony canal of the cochlea
References



:watermark(/images/watermark_only_413.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/lamina-propria-8/BIVdm8ccjhsXHNgEc9Aiw_Lamina_propria__2_.png)